What to expect during a cardiac stress test
If you’ve been experiencing chest pain, breathlessness, or dizziness, without any apparent cause, like rigorous physical activities, your doctor may suggest a cardiac stress test to determine the development of a heart condition. The test is a diagnostic procedure used to measure your heart’s health. So what can you expect during this test? Read on to learn vital aspects of this diagnostic procedure, from what happens during the stress test to how long it takes.
What is a cardiac stress test?
A cardiac stress test is a procedure that is used to assess how well your heart functions while under physical activity or stress. The test is also known as an exercise stress test or tolerance test.
For example, football players tend to undergo this procedure to determine their risk of having a heart attack or stroke. During the test, the footballer’s heart rate is monitored while they perform various activities that exert the heart, such as running on a treadmill or climbing stairs.
What can you expect from the cardiac stress test?
You may wonder what to expect if you’ve been referred for an exercise stress test. Here’s a brief overview of the process.
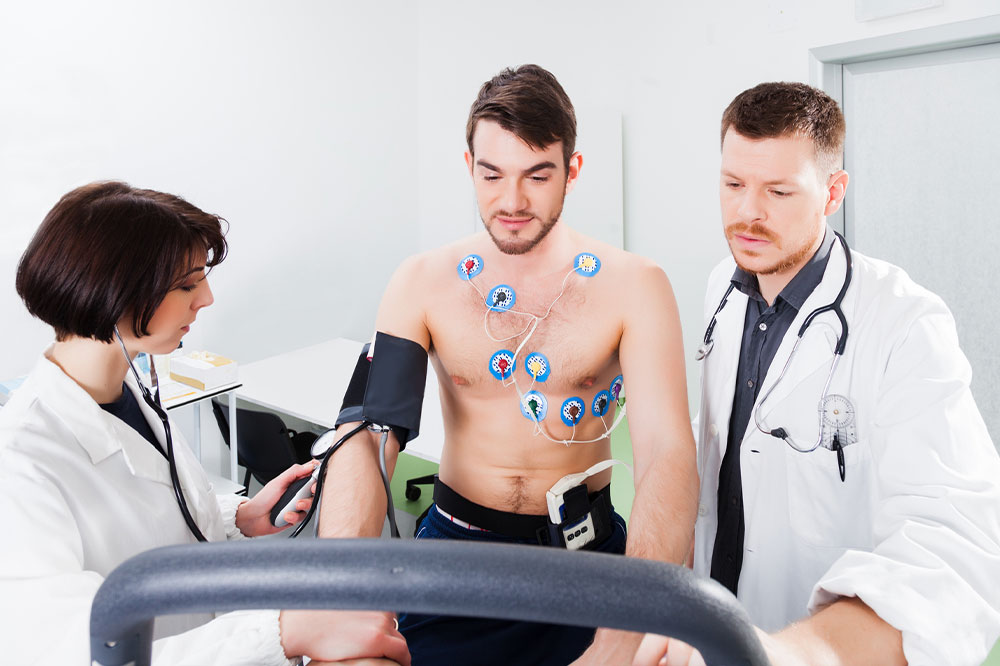
Doctors will ask for your health condition history and conduct a physical examination to determine if you’re a good candidate for the stress test. You’ll be asked to perform the stress test if certain criteria are met.
The aim of the stress test is to see how your heart responds to exercise. The test can also help doctors diagnose other conditions, such as coronary artery disease or arrhythmia.
If you’re scheduled for a cardiac stress test, don’t worry – it’s just a routine procedure to ensure everything is functioning properly with your heart.
How is a cardiac stress test performed?
The exercise tolerance test is usually performed as part of a routine checkup. During the test, your doctor will use a device to measure how well your heart responds to exercise. This can help identify problems with your heart’s rhythm or blood flow.
You’ll be told to take a walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike. Your doctor will closely monitor your progress and make any vital adjustments to the test based on what they see.
During the test, you may experience dizziness, an abnormal heart rhythm, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain. These are all normal reactions to exercise and shouldn’t last long after the test. If you have concerns about the test, talk with your doctor beforehand.
The procedure usually takes about 30 minutes, and you can return to normal activities afterward. You may feel discomfort during the test, but it should not be painful.
After completing a stress test, you can expect to be under observation for a few minutes. The doctor or nurse will tell you to stand still and lie down, and they will monitor your heart rate and blood pressure. You may feel lightheaded or dizzy after the test, but this is normal, and you can go about any regular activities.
Are there any risks involved in a cardiac stress test?
Although there are a few risks associated with cardiac stress tests, they fall into the category of being generally safe.
The complication that is typically an exception is when there is an arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm). Additionally, blood pressure may drop during the test due to increased adrenaline production and other factors. Therefore, don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you have any concerns about your risk or whether a test is appropriate for you. They will monitor it closely and take appropriate measures in case any factor falls outside normal ranges.




